The ICP-MS 2000E is a cutting-edge inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer developed independently by Tianrui. It offers excellent performance at an affordable cost, making it ideal for a wide range of analytical applications. This instrument features an autosampler that enhances automation and improves testing efficiency. Additionally, the latest collision reaction cell technology helps eliminate polyatomic ion interference, reducing detection limits for sensitive elements. The intelligent software comes with pre-integrated application packages, simplifying the sample analysis process and ensuring more reliable data. The ICP-MS 2000E is widely used in environmental monitoring, food safety, semiconductor manufacturing, nuclear industry, petrochemicals, mineral analysis, and medical research.

Figure 1. ICP-MS 2000E Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer
Principle:
In ICP-MS, one of the main sources of interference is polyatomic ions. These can be corrected using mathematical equations or by employing a collision reaction cell. The collision reaction cell introduces a gas (such as helium and hydrogen) into the system, which causes interfering polyatomic ions to dissociate or fragment, thereby reducing their impact on the measurement of the target isotopes. In this study, the ICP-MS 2000E was used to analyze iron, chromium, arsenic, manganese, cadmium, and lead in surface water samples. The He/Hâ‚‚ mixture was employed as the collision gas to minimize argon-based polyatomic interference. The results showed that the detection limit, accuracy, and stability of the method met the required standards.
2. Experiment:
2.1 Reagents and Instruments:
HNO₃ (GR Scharlau);
HCl (GR Scharlau);
Elemental standard solution (10 μg·mLâ»Â¹, from Inorganic Ventures);
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS 2000E, Jiangsu Tianrui Instrument Co., Ltd.);
Laboratory water with a resistivity of 18.25 MΩ·cm (Merck Millipore).
2.2 Sample Pretreatment:
A surface water sample was collected from Kunshan. Following the national environmental testing standard HJ700-2014, the sample was filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, acidified with HNO₃, and adjusted to a pH below 2. Spiked samples were also prepared by adding standard solutions of each element. The concentrations of the spikes were as follows: Sc, Cr, As, Se, Cd, Pb at 4 μg·Lâ»Â¹; Mn at 50 μg·Lâ»Â¹; Fe at 200 μg·Lâ»Â¹; Ni, Zn at 10 μg·Lâ»Â¹.
2.3 Instrument Operating Parameters Optimization:
The instrument was first optimized in standard mode using a tuning solution containing Li, Co, In, U, and Ce at 10 μg·Lâ»Â¹ to maximize sensitivity while keeping oxide and double charge formation below 3%. Then, the He/Hâ‚‚ collision gas was introduced, and the flow rate was gradually increased. The background equivalent concentration at 75 amu was measured using ultrapure water, 4% HCl, and a 10 μg·Lâ»Â¹ As solution in 4% HCl. Further optimization was performed using the As standard solution, and the final working parameters are listed in Table 2.
Table 1. Background Equivalent Concentration at 75 amu in He/Hâ‚‚ Collision Reaction Mode
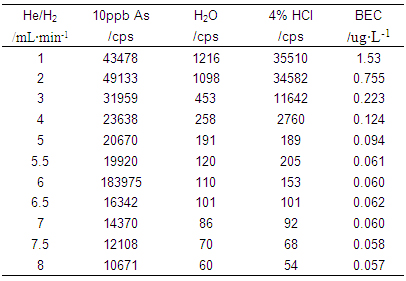
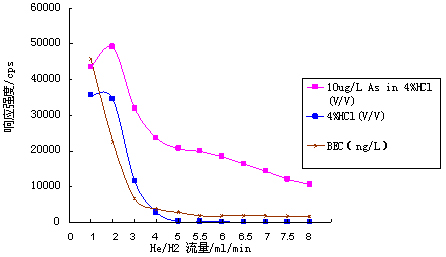
Figure 2. Background Concentration in He/Hâ‚‚ Collision Reaction Mode (BEC is multiplied by 30 times for clarity)
Table 2. Instrument Operating Parameters in Collision Reaction Mode

3. Data and Discussion:
3.1 Argon-Based Polyatomic Interference:
In quadrupole ICP-MS systems, argon plasma is commonly used. Argon atoms can combine with matrix ions to form polyatomic ions, causing interference with the target isotopes. For example, in the case of Cr, Fe, As, and Se, these interferences were observed. Standard solutions of Cr (3% HAc), Fe (1% HNO₃), As (4% HCl), and Se (1% HNO₃) were tested in both standard and collision reaction modes. The results showed that the response intensities of 56Fe and 57Fe were close to their natural abundance ratios, and similarly for 52Cr and 53Cr. This indicates that the use of He/H₂ as a collision gas effectively reduces argon-related polyatomic interference.
Table 3. Argon-Based Polyatomic Interference Ions
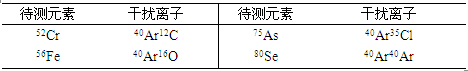
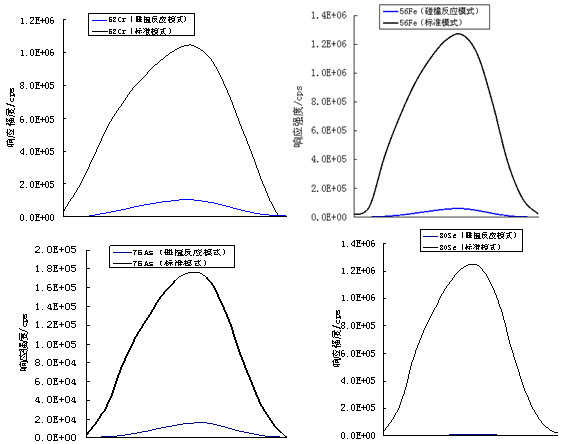
Figure 3. Response Signals of 52Cr, 56Fe, 75As, 80Se in Standard and Collision Reaction Modes
3.2 Recovery Rate and Precision:
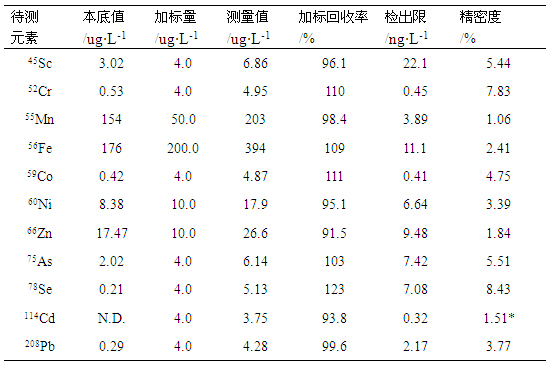
After optimizing the instrument parameters, the sample solution and standard solution were analyzed to determine the recovery rate. Seven blank samples were measured in parallel to calculate the detection limit based on three times the standard deviation of the blank signal. Eleven measurements of the sample solution were taken at 2-minute intervals to evaluate precision. The results showed detection limits ranging from 0.41 to 22.07 ng/L, with recoveries between 93.82% and 123.10%, and relative standard deviations between 1.06% and 8.43%.
Table 4. Standard Recovery and Precision
4. Conclusion:
By optimizing the flow rate of the He/Hâ‚‚ collision gas, argon-based polyatomic ion interference was effectively reduced, allowing accurate measurement of key isotopes such as Fe and Se. Through evaluation of detection limits, recovery rates, and precision, it was confirmed that the ICP-MS 2000E, when operated in collision reaction mode, can successfully mitigate polyatomic ion interference and meet the requirements of industrial analysis in surface water samples.
Zippered Cable Repair Patch
Zippered Cable Repair Patch,Heat-shrink tube,Heat shrinkable tubing,thermal contraction pipe,Shrink tube
Mianyang Dongyao New Material Co. , https://www.mydyxc.com