------ [Guidance] ------
We have all experienced transformative changes. The Internet has been reshaping culture and commerce since the early 1990s, but few people understand how to fully leverage RFID technology to meet the demands of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In the next two decades, the rise of intelligent factories will become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
As the backbone of China’s industrial sector, the manufacturing industry is facing intense competition both domestically and globally. In recent years, market demands have grown more complex, and relying solely on traditional software-based management systems has not been sufficient to achieve optimal efficiency in production.
One major challenge is the inability to track production performance and real-time data across the supply chain. This lack of synchronization leads to inefficiencies such as overproduction, idle time, excessive material movement, and poor inventory control. These issues make it difficult for management to implement precise planning for production, storage, and material flow.
The core issue lies in the lack of real-time and accurate data collection. Without this, even powerful Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems cannot function effectively. Instead, they add to the workload of other departments, creating new inefficiencies and waste.
RFID technology and web-based systems have evolved separately for over 70 years. The earliest use of RFID can be traced back to a British secret project during World War II, which used it to identify friendly or enemy aircraft. Now, with the Fourth Industrial Revolution, these two technologies are being combined to bridge the physical and digital worlds seamlessly.
RFID systems enable automatic identification and data storage without manual intervention, using wireless communication. They allow for real-time data transmission and tracking, making them ideal for improving manufacturing processes. The application of RFID in manufacturing is typically closed-loop, with tags that can be reused, reducing long-term costs.
In the "contactless" information collection method of RFID, electronic tags act as mobile data carriers, aligning well with modern manufacturing needs. RFID helps reduce labor, eliminate human errors, and provide accurate, fast, and reliable data—significantly enhancing the efficiency of high-volume, high-speed production.
The Role of IoT and RFID in Manufacturing
As large-scale industrial production continues to evolve, production lines must adapt to handle multiple product types. This requires clear visibility of each product's status at every stage of the process to ensure correct operations.
Initially, production process cards were used to guide operators. However, this manual approach often led to errors, affecting product quality. RFID technology allows for reading the current status of a product, including its past and future operations, stored in an electronic tag.
RFID enables full automation of production tracking. All operational data can be written into the RFID tag, transmitted to the reader via middleware, and integrated into the company’s existing information system. This enhances quality control and increases productivity while optimizing asset utilization.
Traditional Management in Manufacturing
In traditional manufacturing settings, each station follows a fixed process, producing products with limited variety. Management focuses on product, quality, warehouse, fleet, and after-sales service. Data is manually recorded, leading to errors that affect product quality. A diagram illustrating the traditional production model is shown below:
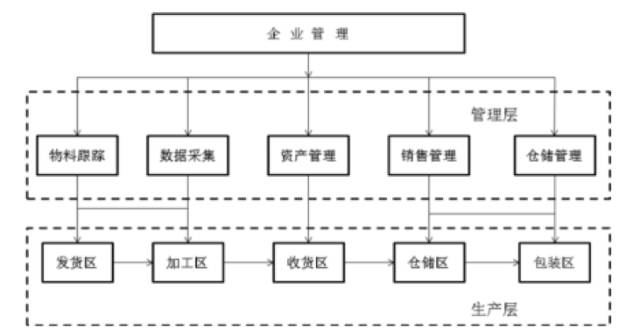
Figure: Traditional Production Operation Model
Challenges of the Traditional Model Include:
Material Tracking
Manual recording of materials leads to delayed updates, resulting in inefficient allocation and excess or insufficient inventory. Errors in tracking make it hard to trace defective parts, impacting product quality.
Warehouse Management
Manual records prevent real-time access to inventory data, causing inefficiencies and increased costs due to overstocking or understocking.
Data Collection
Delayed manual data entry prevents real-time monitoring, limiting quality control and increasing risks when handling multiple product types.
Sales Management
Manual record-keeping reduces sales efficiency and hinders timely production planning, increasing operating costs and slowing cash flow.
Asset Management
Without real-time data, equipment maintenance and material supply planning are inefficient, leading to frequent inspections and higher costs.
Post-RFID Management Status
According to the American Manufacturing Research Institute, real-time data from RFID can improve supply chain performance by 15% in inventory reduction, 17% in order fulfillment, and 35% in cash cycle improvement.
RFID technology is transforming traditional manufacturing by integrating with existing systems through middleware. This allows real-time data access, better planning, and improved productivity.
(1) Real-Time Information Management
RFID enables continuous tracking of products, automatically recording each step and sending data to the management system. This allows for real-time monitoring, better quality control, and efficient decision-making.
(2) Multi-Product Production on the Same Line
With RFID, different products can be processed on the same line without downtime. Tags help identify the type of product and required steps, increasing efficiency and reducing delays.
(3) Real-Time Quality Control
RFID ensures accurate use of resources and provides online testing, ensuring consistent product quality throughout the production line.
(4) Product Tracking and Traceability
RFID allows full tracking of products, making it easy to identify defects and trace their origin. This improves quality control and facilitates recall procedures if needed.
(5) Asset Management
RFID provides real-time data on equipment status, helping to optimize maintenance schedules and improve asset utilization.
(6) Inventory Visibility
RFID supports end-to-end tracking of materials, production, and logistics, enabling better planning and reducing unnecessary costs.
We have all experienced revolutionary shocks. The Internet has transformed culture and commerce since the early 1990s, but few people understand how to fully embrace RFID to meet the challenges of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In the coming decades, the emergence of smart factories will play a central role in global manufacturing.
Pmic Hot Swap Controllers,Pmic Hot Swap Controllers Ec-Mart,Management Pmic Hot Swap Controllers,Hot Swap Voltage Controllers
Shenzhen Kaixuanye Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.icoilne.com