01
- The Brain in the Tank
Long ago, a philosopher proposed an intriguing thought experiment. Imagine a mad scientist, an advanced AI, or an alien being removes a brain from a body and places it in a tank filled with nutrient solution to keep it alive. This brain is then connected to a supercomputer that sends sensory signals through its nerves, mimicking real-world experiences. The brain receives feedback as if it were living normally. Is it possible for the brain to realize it's in a simulated reality?
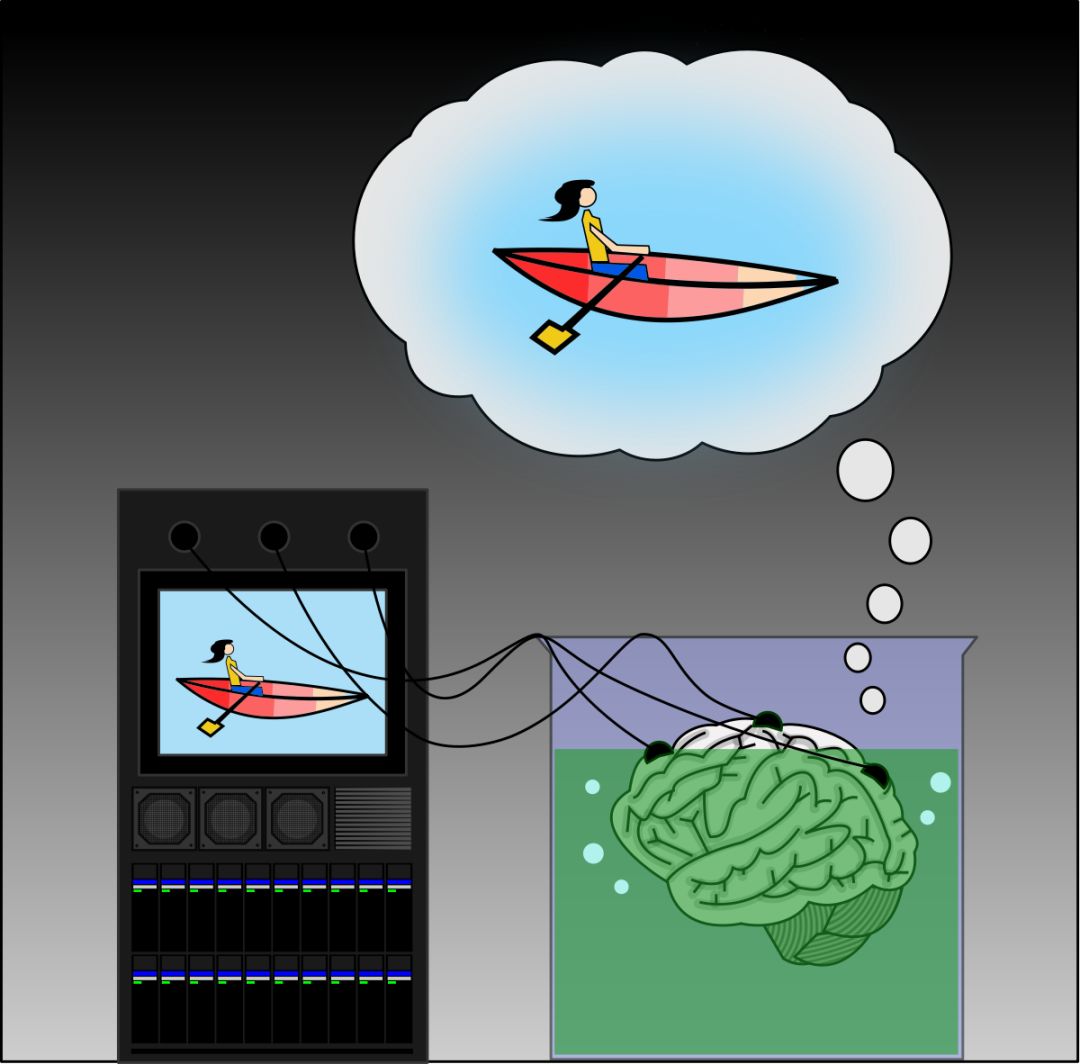
Because of the sensory inputs and corresponding feedback, the brain believes it is experiencing the real world. If the input and feedback are comprehensive and realistic enough, the virtual environment can feel just as real as the physical one. In a way, everything we perceive could be an illusion.
Though this idea sounds extreme and currently impossible due to technical and ethical limitations, it echoes modern technologies like VR. Today, VR is becoming increasingly popular.
What is VR? Simply put, it stands for Virtual Reality, which means "virtual reality" in Chinese. It uses technology to create simulated environments that trick the brain into feeling immersed in a real experience. Users can interact with these virtual worlds, making them feel more authentic.
02
- What is VR?
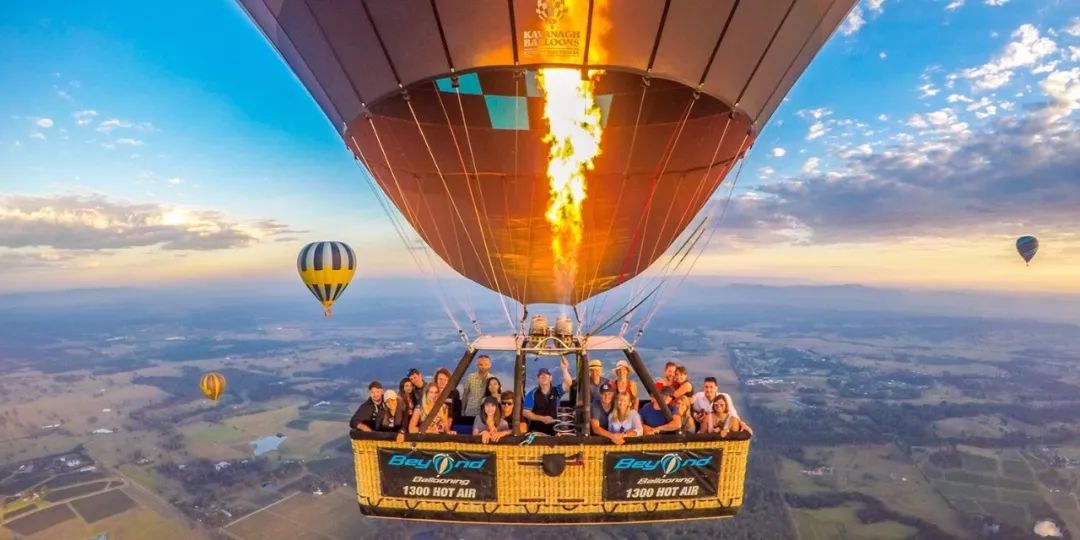
Let’s take an example from the 2018 Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona, Spain. One of the hot VR applications was called “Flying Eagle Canyon.†It simulates flying in a hot air balloon high above the African canyons, cities, and rainforests.
There's a real 1:1 hot air balloon cockpit and a control system that allows users to operate the balloon. Everything you touch—like the seat and fuel—is real. However, what you see, hear, and feel, such as the sensation of acceleration or weightlessness, is all virtual.
When you press the start button, the balloon ignites and ascends. You see flames on the balloon, feel their warmth, and experience the wind. From a 720° view, you can admire the canyon, the blue sky, and clouds above, the bustling passengers beside you, and other balloons nearby.
Although you're sitting in a simulation cockpit at the exhibition, your brain fully immerses itself in the virtual world, believing everything is real.
What you see and hear is like this:

In fact, you’re wearing a VR headset in a showroom, immersed in a virtual world. Bystanders might find it silly, but the experience is genuine for those involved.

Through this example, you now have a clear understanding of VR. But how does the industry define its characteristics?
VR has three main features known as "3I": Immersion, Interaction, and Imagination.
Immersion
Immersive experiences come from machines deceiving the brain by simulating sensory inputs, making the brain believe what it sees, hears, and feels is real. Thus, the user becomes fully engaged in the virtual world.
We perceive the world through our eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and body. These senses include visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, touch, and more complex ones like balance, temperature, and motion. Among these, vision and hearing account for over 90% of our perception. As the saying goes, seeing is believing, and hearing is second only to seeing in importance.
Therefore, VR equipment mainly focuses on visual and auditory inputs, creating 360° immersive visuals and spatial audio, making the brain believe it is in a real environment.
Interaction
Even if the virtual world is immersive, if it cannot be touched or interacted with, the brain will eventually realize it's an illusion. This reduces the sense of immersion and enjoyment.
Thus, VR must provide various input devices that track hand movements, body actions, and provide feedback within the virtual world.
For instance, if you raise a gun and aim at a zombie, the zombie falls. If you pick up a stone, you can feel its hardness and weight. Touching a virtual girlfriend should give you the feeling of her soft skin and warm body.
These interactions make the virtual world more realistic and imaginative, enhancing the fun of VR.
Imagination
Beyond immersion and interaction, another key feature of VR is imagination.
VR breaks free from simulating reality. It can simulate scenes that don’t exist in the real world, creating new possibilities. This allows the brain to experience things in completely different ways, opening up magical applications.
03
- How Did VR Get Started?
Just like every pig that flies up in the wind, VR has had its share of ups and downs. Its history is longer than most people imagine.
First Stage: Fantasy
In 1932, British writer Aldous Huxley mentioned in his novel "Brave New World" a future where people use head-mounted devices to experience movies with images, scents, sounds, and more, making them feel immersed.

In 1935, American writer Stanley Weinbaum wrote a science fiction story called "Pygmalion's Glasses," describing a pair of glasses that let the wearer enter a movie, see, hear, smell, and touch, even communicate with characters.

These stories laid the foundation for VR's immersive experience. The devices described by these creative minds are essentially today's VR helmets.
Second Stage: Emergence
In 1963, futurist Hugo Gensback invented "Teleyeglasses," a head-mounted TV device. Though not as advanced as today's VR, it planted the seeds of VR technology.

In 1965, American scientist Ivan Sutherland proposed a theory about human-computer interaction. Later, the US Air Force used VR for flight simulations.
In 1968, Sutherland developed the "Sword of Damocles," a head-mounted display with stereo imaging and head tracking.
This early device was heavy and needed to be hung from the ceiling, but it closely resembled today's VR gear.
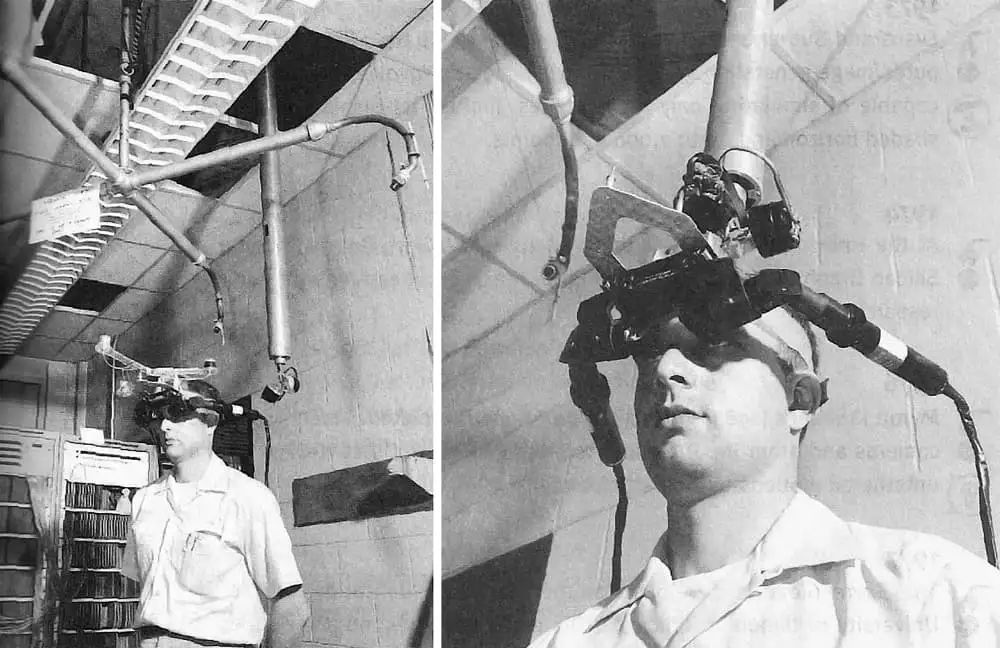
Through the efforts of these pioneers, VR moved from fiction to reality.
Third Stage: Breakthrough
In 1982, the film "Tron" introduced VR to the public, significantly boosting its popularity. Throughout the 1980s, VR became a big trend in the tech world.

In 1983, the US Department of Defense and Army developed a simulation network, while NASA created a VR system for Mars exploration.

In 1984, VPL Research launched VR products like data gloves, VR headsets, and 3D engines, making VR accessible to civilians.

Though expensive, these products laid the groundwork for VR's future.
Fourth Stage: Growth
In the 1990s, VR experienced a surge in popularity with VR arcades. Companies also invested in VR development.
In 1994, VR modeling language emerged, laying the foundation for graphic data transmission. In 1995, Nintendo launched the Virtual Boy, though it failed to gain market traction.

In 1998, Sony released a VR device, and the 1999 film "The Matrix" showcased VR in a compelling way, inspiring the industry.

Despite initial failures, the 1990s laid a solid foundation for VR's future growth.
Fifth Stage: Dormancy
In the early 2000s, VR seemed to fade as smartphones rose in popularity. Despite this, research continued in medical, flight, manufacturing, and military fields.
In 2006, the US Department of Defense launched a VR training program to improve crisis response. In 2008, psychologists used VR to treat PTSD patients.

These examples show that VR was quietly growing, preparing for its next breakthrough.
Sixth Stage: Explosion
In 2014, Facebook acquired Oculus for $2 billion, sparking a VR revolution. With smartphone advancements, VR components became cheaper, making VR more accessible.
In the same year, Google launched Cardboard, Samsung launched Gear VR, and consumer-grade VR began to emerge.

By 2015, Goldman Sachs predicted a VR boom, and 2016 was hailed as the first year of VR. At the 2018 MWC, Huawei demonstrated cloud VR, reducing hardware requirements and making VR more accessible.

After decades of development, VR is finally taking off with the help of 5G technology.
04
- What Can VR Do?
Two Core Needs
Games have always driven technological innovation. Young people around the world thrive with games, from small arcade machines to large online games and mobile games. The magic of games is undeniable.

Previously, video games evolved from one screen to another, with little change in gameplay. VR games are completely different.
Take the medieval combat game "Warrior" as an example. You are in the middle of battle, surrounded by enemies, able to turn around and look around 360°, walk around, and swing your arms to attack.
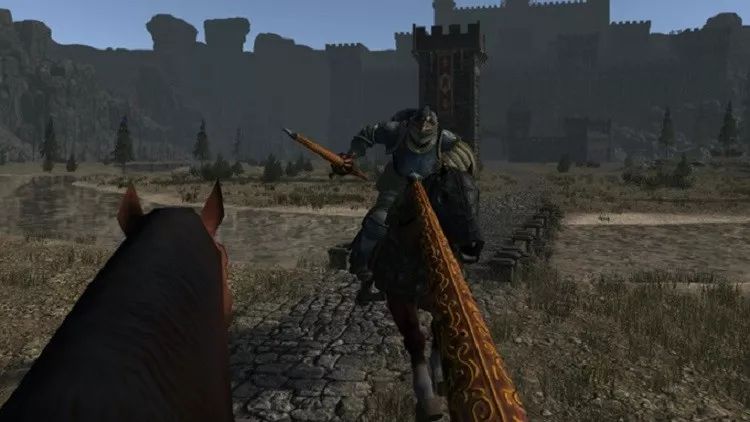

This is a totally different experience, with multi-sensory interactions creating a strong sense of immersion. Of course, the virtual world is infinite, and your room is limited. VR games require special equipment to track movement, so actual movement is restricted.

It may seem silly, but while exercising, you also get the thrill of being like a real character in the game. That's what makes it "cool."
Another form of "cool" is more direct and original. You probably guessed it: VR adult content. It's a stronger driver than games because it caters to a broader audience.

According to statistics, traffic on adult websites exceeds one-third of the global internet. The largest site has 4.4 billion monthly visits, surpassing CNN and ESPN. Its traffic dwarfs YouTube.

With the rise of VR devices, Google Trends data from July 2016 showed a 9900% increase in searches for "VR porn" in 17 months.
Currently, VR videos and games have become standard content for adult sites. Rich content drives technological advancement and hardware popularity, which in turn promotes content growth. This cycle greatly benefits the VR industry chain.
Besides games and adult content, what other areas can consumer-grade VR be used for?
Entertainment & Live Events
VR will allow people to experience live concerts and sports events in an immersive way. With 360° cameras, you can capture the scene and create VR videos for global live broadcasts.

At the 2018 Pyeongchang Winter Olympics, even if you weren't there, you could enjoy a better viewing experience with a VR headset.
Shopping & Advertising
With VR, online shopping may change. Instead of clicking a mouse, you can see and touch real products in a virtual store.

Imagine at a car show, you can test drive different models and road conditions without leaving your home, breaking time and space constraints.
Travel & Exploration
Virtual tourism will become a reality. You can explore European styles, Hawaiian beaches, and African landscapes, or even dive deep underwater or explore Mars.

Whether it's a live 360° video or a computer-generated scene, VR lets you escape the real world and visit your favorite destinations from home.
Education & Simulation
In education, VR can visually construct amazing worlds for learning, such as exploring the universe, ancient Egypt, or performing virtual surgeries safely.

VR teaching allows low-cost learning and practice in any field.
05
- Want to Try a Set of VR Equipment?
Now, what is the current state of VR? Is it a good time to buy a set and try it out?
In 2014, Facebook's acquisition of Oculus stimulated the market. In 2016, it was called the first year of VR. Everyone expected VR to explode in the next one to two years.
However, VR seems to have moved from the previous hype to a new phase of decline. In 2017, the VR industry remained stable, and it's expected to face at least three to five years of stagnation.
The main reasons are slow progress in hardware cost reduction and technology adoption, high costs for content creation, unclear profit models, and a lack of high-quality content. In short, VR is still in its early stages.
Current VR devices are roughly divided into three categories: mobile VR, PC VR, and standalone VR.
Mobile VR
Mobile VR is a low-cost entry-level device that uses a phone as a display, combined with lenses inside the VR headset. Apps on the phone achieve the VR effect.

Google's Cardboard was the originator of mobile VR. Though made of paper, it can still transport you into a virtual world with a phone.

Mobile VR devices are also known as VR glasses. Due to their low cost, software and content have flourished.
Examples include Samsung's Gear VR, Storm Mirror, and Xiaomi's VR glasses. Many VR video apps are available on major video platforms, making it affordable to buy a VR headset as a novelty.
PC VR
PC VR is a headset with display and motion tracking, with content processed by a separate computer. This setup achieves the highest performance and immersive experience.
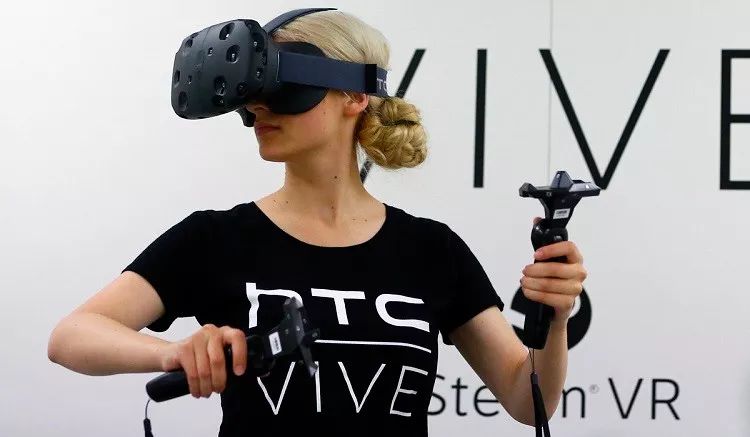
The effect is great, but the price is high. For example, the HTC Vive costs 5488 yuan after a discount. To use it, you need a high-performance computer, costing between 5000 to 10000 yuan.

Thus, to enjoy the ultimate VR gaming experience, you need to spend 10,000 to 15,000 yuan, which is a significant investment, suitable only for serious gamers.
Standalone VR
Standalone VR integrates display and content processing in a compact headset, similar to a combination of a PC and a headset.
Though less powerful than PC VR, it's more portable and easier to use than mobile VR. Prices are relatively more attractive. For example, iQiyi's 4K HD standalone VR costs around 3000 yuan, and Facebook's Oculus Go is priced around 1000 yuan, making it more accessible to the general public.
At the 2018 CES, Xiaomi announced the release of a Xiaomi VR headset in collaboration with Oculus.

With Xiaomi's pricing strategy, it's likely to attract a large fan base, promoting VR's popularity in China.
06
- Summary
VR, or Virtual Reality, offers immersive experiences in video and gaming, characterized by immersion, interaction, and imagination.
VR originated long ago, and after over 80 years, it's still in the stage of equipment and content popularization.
VR has wide applications, including entertainment, live events, shopping, travel, education, and more. Games and videos are the biggest drivers.
Consumer VR devices are mainly divided into mobile VR, PC VR, and standalone VR. Curious users can try mobile VR, gamers can invest in PC VR, and average users can opt for standalone VR.
Withstand high voltage up to 750V (IEC/EN standard)
UL 94V-2 or UL 94V-0 flame retardant housing
Anti-falling screws
Optional wire protection
1~12 poles, dividable as requested
960 Series Terminal Blocks,Electrical Terminal Strips,Electronic Terminal Blocks,Nylon Terminal Block,ballast terminal blocks
Jiangmen Krealux Electrical Appliances Co.,Ltd. , https://www.krealux-online.com